What Is A Full Format Camera
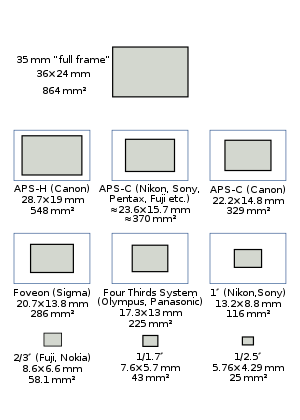
The sizes of sensors used in most current digital cameras, relative to a 35 mm format
A full-frame DSLR is a digital single-lens reflex camera (DSLR) with a 35 mm prototype sensor format (36 mm × 24 mm).[1] [two] Historically, 35 mm was considered the standard film format, in contrast with bigger formats, such as medium format, large format and fifty-fifty larger. However, due to the decreasing popularity of analog photography in favor of digital photography, the format is now leaning towards professional person users, due to the college prices of digital full-frame bodies.
The full-frame DSLR is in contrast to total-frame mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras, and DSLR and mirrorless cameras with smaller sensors (for instance, those with a size equivalent to APS-C-size film), much smaller than a full 35 mm frame. Many digital cameras, both meaty and SLR models, employ a smaller-than-35 mm frame as information technology is easier and cheaper to manufacture imaging sensors at a smaller size. Historically, the earliest digital SLR models, such as the Nikon NASA F4 or Kodak DCS 100, also used a smaller sensor.
Kodak states that 35 mm moving picture (note: in "University format", 21.0 mm × 15.2 mm) has the equivalent of 6K horizontal resolution, according to a senior vice president of IMAX.[3] This equates to 10K horizontal resolution in full-frame size.
Use of 35 mm film-camera lenses [edit]
If the lens mounts are compatible, many lenses, including manual-focus models, designed for 35 mm cameras can be mounted on DSLR cameras. When a lens designed for a full-frame camera, whether picture or digital, is mounted on a DSLR with a smaller sensor size, only the center of the lenses image circle is captured. The edges are cropped off, which is equivalent to zooming in on the centre section of the imaging area. The ratio of the size of the total-frame 35 mm format to the size of the smaller format is known equally the "crop factor" or "focal-length multiplier", and is typically in the range i.3–2.0 for non-total-frame digital SLRs.
Advantages and disadvantages of full-frame digital SLRs [edit]
35 mm lenses [edit]

An APS-C format DSLR (left) and a full-frame DSLR (correct) show the divergence in the size of the sensors.
When used with lenses designed for full frame film or digital cameras, total-frame DSLRs offer a number of advantages compared to their smaller-sensor counterparts. Ane advantage is that wide-angle lenses designed for total-frame 35 mm retain that aforementioned broad angle of view. On smaller-sensor DSLRs, wide-angle lenses have smaller angles of view equivalent to those of longer-focal-length lenses on 35 mm film cameras. For example, a 24 mm lens on a camera with a crop factor of ane.five has a 62° diagonal angle of view, the same as that of a 36 mm lens on a 35 mm film camera. On a total-frame digital camera, the 24 mm lens has the same 84° angle of view equally it would on a 35 mm film photographic camera.
If the same lens is used on both full-frame and cropped formats, and the subject distance is adjusted to have the same field of view (i.e., the aforementioned framing of the subject field) in each format, depth of field (DoF) is in inverse proportion to the format sizes, so for the same f-number, the total-frame format will have less DoF. Equivalently, for the same DoF, the full-frame format will require a larger f-number (that is, a smaller aperture diameter). This human relationship is approximate and holds for moderate subject distances, breaking down as the distance with the smaller format approaches the hyperfocal distance, and as the magnification with the larger format approaches the macro range.


Two photographs with the same lens and ISO, but a different sensor size: upon zooming in (insets), one notices in that location is less noise in the bottom picture (full-frame sensor - Canon EOS 6D) than in the top one (smaller sensor - EOS 7D Mark Two).
There are optical quality implications likewise—not just because the paradigm from the lens is effectively cropped—merely because many lens designs are now optimized for sensors smaller than 36 mm × 24 mm. The rear chemical element of any SLR lens must have clearance for the photographic camera'south reflex mirror to motion upward when the shutter is released; with a wide-angle lens, this requires a retrofocus design, which is generally of junior optical quality.[4] Considering a cropped-format sensor tin have a smaller mirror, less clearance is needed, and some lenses, such equally the EF-South lenses for the Canon APS-C sized bodies,[5] are designed with a shorter back-focus distance; however, they cannot be used on bodies with larger sensors.
The full-frame sensor can likewise be useful with broad-angle perspective control or tilt/shift lenses; in particular, the wider angle of view is oft more than suitable for architectural photography.
While full-frame DSLRs offering advantages for broad-angle photography, smaller-sensor DSLRs offer some advantages for telephoto photography because the smaller angle of view of modest-sensor DSLRs enhances the telephoto result of the lenses. For example, a 200 mm lens on a camera with a crop factor of 1.5× has the same bending of view as a 300 mm lens on a full-frame photographic camera. The extra "attain", for a given number of pixels, can be helpful in specific areas of photography such equally wild animals or sports.[6]
Lower size sensors also let for the use of a wider range of lenses, since some types of optical impurities (specifically vignetting) are almost visible around the edge of the lens. By simply using the middle of the lens, these impurities are not noticed. In practice, this allows for the use of lower price lenses without corresponding loss of quality.[7]
Finally, full frame sensors allow for sensor designs that upshot in lower dissonance levels at high ISO [viii] and a greater dynamic range in captured images. Pixel density is lower on full frame sensors. This ways the pixels can be either spaced further autonomously from each other, or each photodiode can be manufactured at a slightly larger size. Larger pixel sizes tin can capture more light which has the advantage of allowing more calorie-free to exist captured before over saturation of the photodiode. Additionally, less dissonance is generated by adjacent pixels and their emf fields with larger photodiodes or greater spacing between photodiodes. For a given number of pixels, the larger sensor allows for larger pixels or photosites that provide wider dynamic range and lower noise at high ISO levels.[nine] As a consequence, total-frame DSLRs may produce better quality images in certain high dissimilarity or low light situations.
Production costs for a full-frame sensor can exceed twenty times the costs for an APS-C sensor.[ citation needed ] Only xx full-frame sensors will fit on an 8-inch (200 mm) silicon wafer, and yield is comparatively low because the sensor's large area makes it very vulnerable to contaminants—20 evenly distributed defects could theoretically ruin an entire wafer. Additionally, when full-frame sensors were first produced, they required three separate exposures during the photolithography stage, tripling the number of masks and exposure processes.[10] Modern photolithography equipment now allows single-laissez passer exposures for full-frame sensors, but other size-related production constraints remain much the aforementioned.
Some total-frame DSLRs intended mainly for professional person utilise include more features than typical consumer-class DSLRs, so some of their larger dimensions and increased mass result from more rugged structure and additional features as opposed to this being an inherent outcome of the full-frame sensor.
Past and present total-frame DSLRs [edit]
DSLRs [edit]

- Canon EOS-1Ds (2002)
- Canon EOS-1Ds Mark II (2004)
- Catechism EOS-1Ds Marker III (2007)
- Canon EOS-1D X (2012)[11]
- Canon EOS-1D X Marker II (Feb 2, 2016)
- Canon EOS-1D Ten Mark III (January 2020)
- Catechism EOS 5D (2005)
- Canon EOS 5D Mark Two (2008)
- Catechism EOS 5D Marking III (two March 2012)
- Catechism EOS 5Ds / 5Ds R (February 6, 2015)
- Catechism EOS 5D Marker IV (August 2016)
- Canon EOS 6D (17 September 2012)[12]
- Catechism EOS 6D Mark Ii (30 June 2017)
- Contax N Digital (2002)
- Kodak DCS Pro 14n (2003)
- Kodak DCS Pro SLR/c (2004)
- Kodak DCS Pro SLR/n (2004)

The Nikon D6 is Nikon's flagship total-frame DSLR
- Nikon D3 (2007)
- Nikon D3X (2008)[13]
- Nikon D3S (2009)[14]
- Nikon D4 (2012)[15]
- Nikon D4S (February 24, 2014)
- Nikon D5 (January 6, 2016)
- Nikon D6 (February 11, 2020)
- Nikon D800[16] / Nikon D800E (2012)
- Nikon D810 (June 26, 2014)
- Nikon D850 (August 24, 2017)
- Nikon Df (5 November 2013)[17]
- Nikon D700 (2008)
- Nikon D750 (September 12, 2014)
- Nikon D780 (January 2020)
- Nikon D600 (xiii September 2012)[xviii]
- Nikon D610 (8 October 2013)[nineteen]

- Pentax M-1 (February 18, 2016)
- Pentax K-one II (Feb 21, 2018)
- Sony α DSLR-A900 (2008)
- Sony α DSLR-A850 (2009)[20]
- Sony α SLT-A99 / Sony α SLT-A99V (12 September 2012)[21] (utilizing a semi-transparent SLT mirror)
- Sony α ILCA-99M2 (2016)
The Nikon E2/E2s (1994),[22] E2N/E2NS (1996)[23] and E3/E3S (1998)[24] digital SLRs as well as the like Fujifilm Fujix DS-505/DS-515, DS-505A/DS-515A and DS-560/DS-565 models used a reduction optical organization (ROS) to compress a full-frame 35 mm field onto a smaller two/3-inch (xi mm diagonal) CCD imager. They were therefore not digital SLRs with full-frame sensors, notwithstanding had an angle of view equivalent to full-frame digital SLRs for a given lens; they had no crop cistron with respect to angle of view.[25]
The first full-frame DSLR cameras were developed in Nihon from effectually 2000 to 2002: the MZ-D past Pentax,[26] the N Digital past Contax'southward Japanese R6D team,[27] and the EOS-1Ds past Catechism.[28]
Nikon has designated its full frame cameras as FX format and its smaller sensor interchangeable-lens camera formats as DX and CX.
Other technologies [edit]
- Sony Handycam NEX-VG900 (announced September 2012) – a 35mm full-frame video camera (also capable to shoot hi-resolution photos) with interchangeable lenses (Sony Due east-mountain)
- Sony Cyber-shot DSC-RX1 (announced September 2012) and Sony Cyber-shot DSC-RX1R (announced June 2013) – full-frame compact cameras with fixed lens
- Sony Cyber-shot DSC-RX1R 2 – full-frame compact camera with fixed lens from 2015
Features of some full frame DSLR cameras [edit]
| Brand | Model name | Sensor size | Constructive megapixels | Lens mount | Viewfinder coverage | Metering zones | Focus points | Lowest ISO | Highest ISO | DxO score | DxO ISO [29] | Cont. shtg | LCD size | LCD joint method | Alive view | Movie fashion | Retentiveness menu | Video | Dimensions (mm) | Weight (g; incl. Battery?)[30] | Announced (date) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catechism | 5D Mark IV | Full frame | 30.ane | EF | 100 | 252 | 61 | 50 | 102,400 | 91 | 2995 | 7 | 3.2 | None | aye | yes | CF+SD | 150.vii×116.4×75.9 | 890 | Aug 2016 | [1] | |
| Canon | 1D X Mark 2 | Full frame | twenty.2 | EF | 100 | 216 | 61 | 50 | 409,600 | 88 | 3207 | 14 | 3.2 | None | yes | yep | CF+CFast | 158x168x83 | 1530 | Feb 2016 | [1] [2] | |
| Catechism | 1D 10 | Total frame | xviii.i | EF | 100 | 252 | 61 | 50 | 204,800 | 82 | 2786 | 14 | iii.2 | None | yes | yes | CF (2x) | 158x164x83 | 1530 | Oct 2011 | [three] [4] | |
| Canon | 1Ds Marker Iii | Full frame | 21.1 | EF | 100 | 63 | 45 | 50 | 3,200 | lxxx | 1663 | 5 | 3 | None | yes | no | CF+SD | 150x160x80 | 1205 | Aug 2007 | [v][6] | |
| Canon | 5D Marker Three | Full frame | 22.three | EF | 100 | 63 | 61 | 50 | 102,400 | 81 | 2293 | vi | iii.two | None | yes | yes | CF+SD | 152x117x77 | 950 (860 without battery) | Mar 2012 | [7][viii] | |
| Canon | 5D Mark II | Full frame | 21.ane | EF | 98 | 35 | 9 | 50 | 25,600 | 79 | 1815 | 3.nine | 3 | None | yeah | yep | CF | 152x114x75 | 810 | Sep 2008 | [9][10] | |
| Canon | 6D | Full frame | 20.two | EF | 97 | 63 | 11 | 50 | 102,400 | 82 | 2340 | 4.5 | iii | None | yeah | yeah | SD | 145x111x71 | 755 (680 without bombardment) | Sep 2012 | [eleven] | |
| Nikon | D5 | Full frame | 20.8 | F-mount | 100 | 180,000 | 153 | 50 | 3,280,000 | 88 | 2434 | 12 | 3.two | None | yep | aye | SD (2x) or XQD (2x) | 2160p30 | 160x159x92 | 1405(with battery) | Feb 2017 | [12] |
| Nikon | D4 | Full frame | xvi.2 | F-mount | 100 | 91,000 | 51 | l | 204800 | 89 | 2965 | 11 | 3.2 | None | yes | yeah | CF + XQD | 160x157x91 | 1180 (without bombardment) | January 2012 | [13] [14] | |
| Nikon | D3X | Total frame | 24.iv | F-mount | 100 | 1,005 | 51 | 50 | 6,400 | 88 | 1992 | five | 3 | None | yes | no | CF (2x) | 160x157x88 | 1220 | December 2008 | [xv][16] | |
| Nikon | D3S | Full frame | 12.1 | F-mountain | 100 | 1,005 | 51 | 100 | 102,400 | 82 | 3253 | 9 | 3 | None | yes | yes | CF (2x) | 160x157x88 | 1246 | Oct 2009 | [17][xviii] | |
| Nikon | D850 | Full frame | 45.7 | F-mountain | 100 | 180,000 | 153 | 64 (32 with expansion) | 25,600 | 100 | 2660 | 7 | iii.2 | Tilting | yep | yes | CF + XQD | 2160p30 | 146x124x79 | 1005 | Oct 2017 | [19] |
| Nikon | D810 | Total frame | 36.three | F-mount | 100 | 91,000 | 51 | 64 | 51,200 | 5 | 3.two | None | yeah | yes | CF + SD | 1920p60 | 146x123x82 | 980 | [20] | |||
| Nikon | D800 | Full frame | 36.three | F-mount | 100 | 91,000 | 51 | 50 | 25,600 | 95 | 2853 | iv | three.2 | None | aye | yep | CF + SD | 145x122x82 | 900 (without battery) | Feb 2012 | [21] [22] [23] | |
| Nikon | D780 | Total frame | 24.3 | F-mountain | 100 | 91,000 | 51 | 100 | 51,200 | 7 | three.2 | Tilting | yes | yes | SDXC (2x) | 143.4x115.5x76 | 840 incl. Batt. | Jan 2020 | ||||
| Nikon | D750 | Full frame | 24 | F-mount | 100 | 91,000 | 51 | 100 | 12,800 | 93 | 2956 | 6.5 | 3.ii | Tilting | yes | yes | SD (x2) | 141x113x78 | 840 incl. Batt. | Sep 2014 | [24][25] | |
| Nikon | D700 | Total frame | 12.ane | F-mountain | 95 | i,005 | 51 | 100 | 25,600 | eighty | 2303 | 5 | 3 | yep | no | CF | 147x123x77 | 995 | Jul 2008 | [26][27] | ||
| Nikon | D600 | Full frame | 24.3 | F-mount | 100 | ii,016 | 39 | 50 | 25,600 | 94 | 2980 | 5.5 | 3.2 | yes | yeah | SD (x2) | 141x113x82 | 850 incl. Batt. | Sep 2012 | [28] [29] | ||
| Pentax | Grand-1 | Full frame | 36.three | K mount | 100 | 86,000 | 33 | 100 | 204,800 | 96 | 3280 | iv.4 | three.2 | Cross-tilt | yep | aye | SDXC (2x) | 1080p30 | 136.5x110x85.5 | 1010 incl. Batt. | Sep 2016 | [30][31] |
| Pentax | K-ane II | Full frame | 36.3 | Yard mount | 100 | 86,000 | 33 | 100 | 204,800 | 96 | 3280 | 4.4 | three.2 | Cross-tilt | yes | yes | SDXC (2x) | 1080p30 | 136.5x110x85.five | 1010 incl. Batt. | Feb 2018 | |
| Sony | Alpha 900 | Full frame | 24.6 | Sony α/Minolta A | 100 | xl | 9 | 100 | 6400 | 79 | 1431 | 5 | 3 | no | no | CF, MS | 156x117x82 | 895 incl. Batt. | Sep 2008 | [32] [33] | ||
| Sony | Alpha 850 | Total frame | 24.half dozen | Sony α/Minolta A | 98 | 40 | nine | 100 | 6400 | 79 | 1415 | 3 | 3 | no | no | CF, MS | 156x117x82 | 895 | Aug 2009 | [34][35] | ||
| Brand | Model name | Sensor size | Effective megapixels | Lens mount | Viewfinder coverage (% of the frame) | Metering zones | Focus points | Lowest ISO | Highest ISO | DxOMark sensor score | DxO ISO performance[31] | Cont. shtg (fps) | LCD size (in) | LCD articulation method | Live view | Moving picture mode | Retentiveness carte type | Video | Dimensions (mm) | Weight (g)[32] | Announced (date) | Reference |
Prototype full-frame digital SLRs [edit]
- Pentax MZ-D "MR-52" (presented in 2000, based on Pentax MZ-S, with the aforementioned sensor as Contax N, it never went into product)[33]
- Sony Alpha flagship model "CX62500" (presented at PMA 2007, early prototype of what 1-and-a-half years after became the DSLR-A900 (aka "CX85100"), though with many detail differences)[34] [35]
See likewise [edit]
- Full-frame mirrorless interchangeable-lens camera
- Paradigm sensor format
References [edit]
- ^ Nigel Atherton; Steve Crabb; Tim Shelbourne (2006). An Illustrated A to Z of Digital Photography: People And Portraits. Sterling Publishing Co. Inc. ISBN2-88479-087-X.
- ^ Ross Hoddinott (2006). Digital Macro Photography. Sterling Publishing Co. Inc. ISBNone-86108-452-viii.
- ^ "/Film Interview: IMAX Executives Talk 'The Hunger Games: Catching Fire' and IMAX Misconceptions". Slash Film. 2013-12-02. Retrieved 2013-12-17 .
- ^ "Retrofocus Blueprint Problems: A Synopsis". Camerarepair.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-03. Retrieved 2010-12-30 .
- ^ "The Canon Photographic camera Story: 2001-2004". November 2004. Archived from the original on 2009-07-09. Retrieved 2009-09-26 .
- ^ Barbara Gerlach (2007). Digital Nature Photography: The Fine art and the Scientific discipline. Focal Printing. p. 67. ISBN978-0-240-80856-7.
- ^ Bourne, Scott. "Seven Myths About the Need for Full Frames". Archived from the original on 2016-12-14. Retrieved 2013-10-xv .
- ^ "Studio shot comparison". Nov 2019. Retrieved 2019-02-06 .
- ^ "Full-frame sensors". Photocrati. 2009-05-xi. Retrieved 2010-12-thirty .
- ^ "Canon's Total-Frame CMOS Sensors: The Finest Tools for Digital Photography" (PDF) (Press release). Canon. 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-10-x. Retrieved 2009-12-26 .
- ^ "Canon UsA. Introduces The New Canon EOS-1D Ten Digital SLR Camera, Re-Designed From The Inside Out" (Printing release). Canon U.S.A. 2011-10-eighteen. Retrieved 2011-x-18 .
- ^ "Canon Announces Its Smallest and Lightest Full-Frame Digital SLR Camera For Serious Photographers" (Press release). Canon U.S.A., Inc. 2012-09-17. Retrieved 2012-09-17 .
- ^ "Nikon D3x press announcement as of November 30th, 2008". Printing.nikonusa.com. 2008-11-30. Archived from the original on 2011-01-10. Retrieved 2010-12-30 .
- ^ "Nikon D3s printing announcement as of Oct 14th, 2009". Press.nikonusa.com. 2009-ten-14. Archived from the original on 2011-01-x. Retrieved 2010-12-30 .
- ^ "When There Is No Second Take a chance: The New Nikon FX-Format D4 Multi-Media Digital SLR is The Definitive Unification Of Speed And Precision" (Press release). Nikon Inc. 2012-01-05. Archived from the original on 2012-08-16. Retrieved 2012-01-06 .
- ^ "Expectations Surpassed: The 36.three-Megapixel Nikon D800 Is The Multimedia HD-SLR That Shatters Conventional Resolution Barriers For Maximum Fidelity" (Press release). Nikon Inc. 2012-02-06. Archived from the original on 2011-08-thirty. Retrieved 2012-02-07 .
- ^ "Fall in Love Again: New Df D-SLR is Undeniably a Nikon with Legendary Performance and Timeless Design" (Press release). Nikon Inc. 2013-eleven-04. Retrieved 2013-11-05 .
- ^ "Performance that Fuels the Passion: The New Nikon D600 Puts FX-Format in Focus for Photograph Enthusiasts" (Press release). Nikon Inc. 2012-09-13. Retrieved 2012-09-13 .
- ^ "Concentrate on the Clarity: The New Nikon D610 FX-Format D-SLR Places Emphasis on the Image Making Experience" (Press release). Nikon Inc. 2013-10-08. Retrieved 2013-x-08 .
- ^ "Sony α DSLR-A850 printing announcement every bit of August 27th, 2009". News.sel.sony.com. 2009-08-27. Archived from the original on 2011-07-sixteen. Retrieved 2010-12-xxx .
- ^ "Sony introduces full-frame α99" (Press release). Sony. 2012-09-12. Archived from the original on 2012-09-17. Retrieved 2012-09-17 .
- ^ "Technical information on Nikon E2/E2s and Fujifilm Fujix DS-505/DS-515 at MIR - Photography in Malaysia". Mir.com.my. Retrieved 2010-12-30 .
- ^ "Technical data on Nikon E2N/E2Ns and Fujifilm Fujix DS-505A/DS-515A at MIR - Photography in Malaysia". Mir.com.my. Retrieved 2010-12-30 .
- ^ "Technical information on Nikon E3/E3s and Fujifilm Fujix DS-560/DS-565 at MIR - Photography in Malaysia". Mir.com.my. Retrieved 2010-12-xxx .
- ^ Jarle Aasland, Nikon E2N, NikonWeb.com.
- ^ "The long, difficult route to Pentax full-frame". dpreview.com.
- ^ British Journal of Photography, Issues 7410-7422, 2003, folio ii
- ^ "Canon EOS-1Ds, 11 megapixel total-frame CMOS". dpreview.com.
- ^ ISO value, at which the noise starts to disturb the photo. Unit: ISO. More at DxOMark - Utilize Case Scores
- ^ Data taken from specification pages of Digital Photography Review Archived 2012-06-xiv at the Wayback Car review pages (ordinarily folio #2 of given camera review), e.g. hither for a Nikon D3000
- ^ ISO value, at which the noise starts to disturb the photo. Unit: ISO. More at DxOMark Sensor Scores - Sports & action photography: Low-Light ISO Archived 2013-07-20 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Please specify if bombardment and card included! Data taken from specification pages of Digital Photography Review Archived 2012-06-14 at the Wayback Machine review pages (usually page #ii of given camera review), eastward.g. hither for a Nikon D3000
- ^ Asahi Optical Historical Club (2001) "MR-52" vi Megapixel digital SLR Archived 2009-02-28 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ – Charlie White (2007-03-08). "Charlie White'due south Gizmodo PMA March eighth, 2007 report on Sony press announcement in regard to Sony Alpha flagship model "CX62500"". Gizmodo.com. Retrieved 2010-12-30 .
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Paul, Matthias R. (2009-09-xxx). "Sony Alpha CX model codes overview". Minolta-Forum (in German). Archived from the original on 2016-04-01. Retrieved 2016-01-01 .
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Full-frame_DSLR
Posted by: beadlewhoseeps.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is A Full Format Camera"
Post a Comment